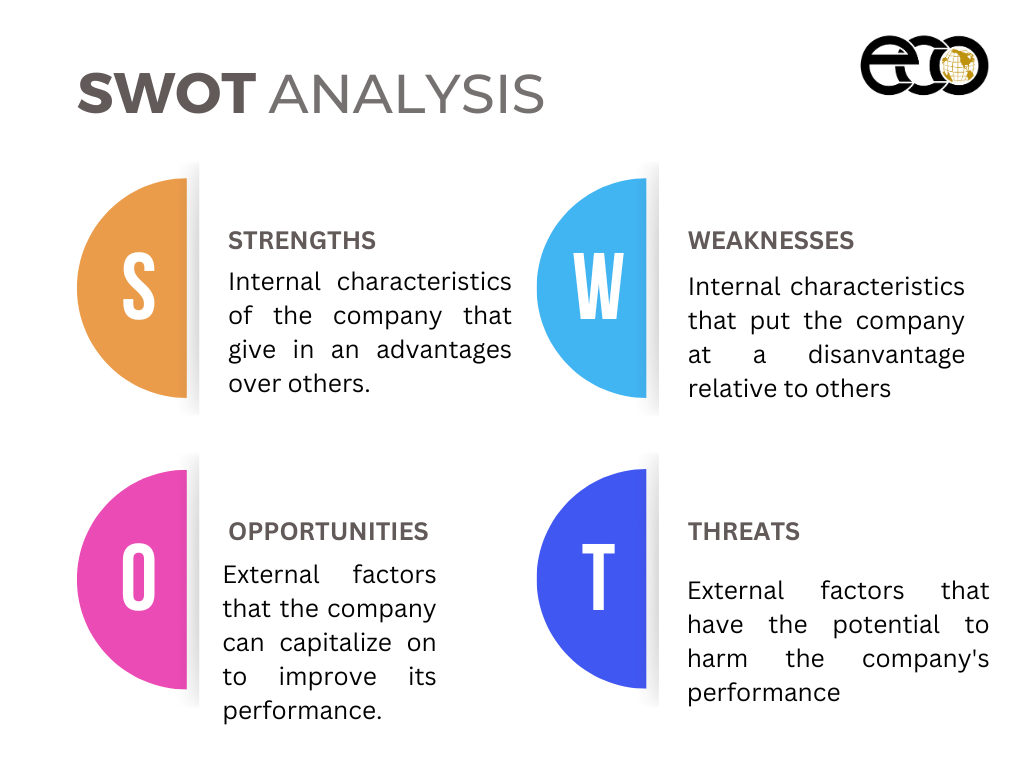
The FODA, FADO, DAFO, and DOFA are Spanish acronyms for classic methodologies of administration. In English, it would be SWOT:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
The SWOT principle is used worldwide in planning company strategies or starting new projects. This is due to its utilization being so varied and applicable anywhere. SWOT provides a diagnostic of the idea and lays out the situation surrounding it. The result of the analyses is the creation of the matrix, also called the SWOT Matrix, which helps identify the main internal factors that need to be worked on and the external points that demand attention. Although it is often said that SWOT and DAFO are the same, there are small differences in how external and internal aspects are addressed.
Both are tools to determine strategies based on the assessment of internal aspects (strengths and weaknesses) and external aspects (opportunities and threats).
The difference lies in the order in which we approach the system. As Michael D. Watkins mentions, following a sequence of weaknesses and then addressing the threats improves the debate and ideas, as opposed to discussions far from reality that result from focusing first on strengths and opportunities.
- S* Strengths D* Debilidades (Weaknesses)
- W* Weaknesses A* Amenazas (Threats)
- O* Opportunities F* Fortalezas (Strengths)
- T* Threats O* Oportunidades (Opportunities)
Michael D. Watkins. (2007). “From SWOT to TOWS”, Harvard Business Review, Issue 2822
Step-by-Step SWOT Analysis
- Step 1: Objective
Analysis of interactions to determine strategies.
The reason why a SWOT analysis is carried out must be clear.
- Step 2: Strengths
Strengths are the internal positive factors.
What distinguishes us positively from others?
- Step 3: Opportunities
Positive factors that must be capitalized on to generate competitive advantage.
Are there favorable trends? Changes in the market?
- Step 4: Weaknesses
These are internal negative factors; consider them.
What are the reasons behind the existing problems?
- Step 5: Threats
Risks that have the potential to cause problems and are generally outside our control.
What are the unfavorable trends that reduce the success of projects?
- Step 6: Strategies
- Success (FO): How to use our strengths to take advantage of our opportunities?
- Adaptation (DO): How to address our weaknesses by taking advantage of the opportunities?
- Reaction (FA): How to use our strengths to mitigate threats?
- Survival (DA): How to minimize weaknesses to face threats?